EAL Literacy Learner Resource
EAL learners with EAL literacy needs are learning English as well as developing reading and writing skills. They do not have fully developed EAL literacy skills in their first language. They are a diverse group, with skills and abilities that range from lacking any reading and writing skills, to having basic EAL literacy skills, but not enough to be considered functionally literate. There are a variety of reasons why learners may lack functional EAL literacy. They may have little to no formal education in their previous countries, have interrupted learning due to war or unrest, or may have had injuries or trauma that resulted in a loss of EAL literacy skills.

The Canadian Language Benchmarks: ESL for Adult Literacy Learners (CLB: ESL for ALL) was developed to provide guidance to instructors who teach learners with EAL literacy needs. Its key assumption is that EAL literacy learners progress through the same CLB levels as literate learners, but have unique needs for EAL literacy skills development. As an instructor of EAL literacy learners, you will still use the CLB framework to plan and assess learning. However, you will also refer to the CLB: ESL for ALL for guidance with providing the extra support and instruction EAL literacy learners need.
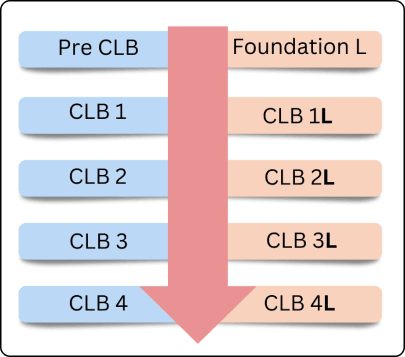
Both literate learners and EAL literacy learners are located on the same CLB scale as shown on the right. An “L” designation indicates the learner’s EAL literacy needs. EAL literacy learners span a range of language and EAL literacy ability, from Foundation L to CLB 4L, and progress through these levels at various speeds, though generally slower than learners without EAL literacy needs.
CLB: ESL for ALL provides guidance to instructors of EAL literacy learners, whether they are teaching a dedicated EAL literacy class, or a course with both literate and EAL literacy learners. It outlines five levels of ability: Foundation L, and CLB 1L-CLB 4L. Foundation L learners have not yet met the requirements for CLB 1, and need to learn the basics of reading and writing, such as recognizing the letters of the alphabet, numbers 1-10, their own name and a few sight words. For CLB 1L-4L, learners work towards the same CLB outcomes as literate learners, but generally at a slower pace and with much more support, instruction and repeated practice of EAL literacy skills. For each level, ESL for ALL lists the characteristics and skill gaps a EAL literacy learner may demonstrate, as well as examples of activities to address those skill gaps.
ESL for ALL also presents an approximate progression (or continuum) of EAL literacy skills and abilities in seven skill areas: oral communication, learning strategies, numeracy, digital literacy, sociocultural knowledge, reading, and writing. These continuums can help you become aware of a range of EAL literacy skills and strategies so that you can determine which skills learners need and develop skill-building activities to help learners develop those skills.
Useful Resources and References
Related Essential Components
External Resources
- Bow Valley College has A Practical Guide to Teaching ESL Literacy
- Bow Valley College has ESL Literacy Readers at a variety of EAL literacy levels
- CCLB: Multilevel Modules include multi-level EAL literacy modules
- CLB: ESL for Adult Literacy Learners
- CLB: ESL for ALL Support Kit provides support and examples for planning EAL literacy instruction and assessing progress
- ISANS has a collection of Literacy Activities
- The Immigrant Education Society has resources, including assessments and full length Literacy Modules
- The Immigrant Education Society has the Literacy Centre of Expertise which provides ongoing professional development and hosts an annual conference
External Courses
- Bow Valley College has a course in ESL Literacy Material Design
- CCLB offers CLB Literacy Training Courses